Member-only story
Since last year, cobalt strike payloads are everywhere. We saw hackers used Cobalt Strike in many attacks. Some serious cyber incident like SolarWinds supply chain attack [1]. In Proofpoint’s new article, said that Cobalt Strike is the favorite tool from APT to crimeware [2]. Cobalt Strike is a penetration tool which developed by Strategic Cyber. It’s a good framework for collaboration by Red team.
In these days, the executable and dll type of cobalt strike payload are most often used in attack. Other’s payload type like macro or powershell sometimes were also be delivered by attackers. In this article, let’s analysis the cobalt strike powershell payload.
Sample
MD5: e0315aca119a9b3b7d89184ad2fa2603
SHA-1: bfc928da46d2ae32e2c60373a5d968d2f15e497a
SHA-256: 24b18a60020d05b32b13d2cf1e6d6b1ccda4f0af5fb5ec0da960746fde54b796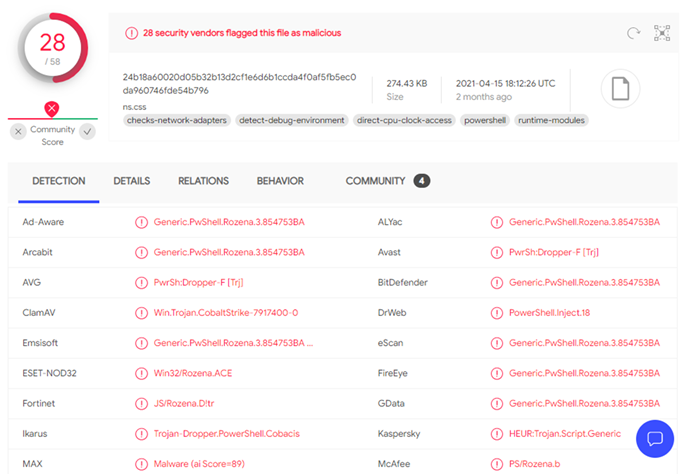
VirusTotal shows there are 28 AV vendors detect this malicious payload. 4 vendors detect it is cobalt strike related malware, and 8 vendors detect it as「PwShell.Rozena」. That’s interesting! After I searched what is Rozena, and I found an analysis report published in 2018 from GDATA [3]. Looks like the malware used some technique of command line to run powershell, performing fileless attacks.
Analysis
You can use your preferred text editor to open this sample. First, I noticed that this sample is not obfuscated, whereas many PowerShell malware variants use obfuscation to evade antivirus detection. Additionally, this sample is a stageless payload [4], meaning it was generated directly by the Cobalt Strike attack package. According to the description on the official Cobalt Strike website, we know that:
Attacks -> Packages -> Windows Executable (S) generates a Windows executable artifact that contains Cobalt Strike’s Beacon (no stagers, hence a stageless payload!). This package gives you several output options.
One of option is PowerShell:
PowerShell is a PowerShell script that injects a stageless Beacon into memory.
As below PowerShellscript (I bypass the big string part in the middle):
